Enhancing Urban Resilience Through Green Roofs and Gardens
Written on
Chapter 1: The Rise of Urbanization and its Challenges
Urbanization is a growing trend, with projections suggesting that by 2050, two-thirds of the global population will reside in cities. This rapid urban expansion often leads to the replacement of natural greenery with artificial structures, disrupting the ecological balance and increasing the demand for water, energy, and food.
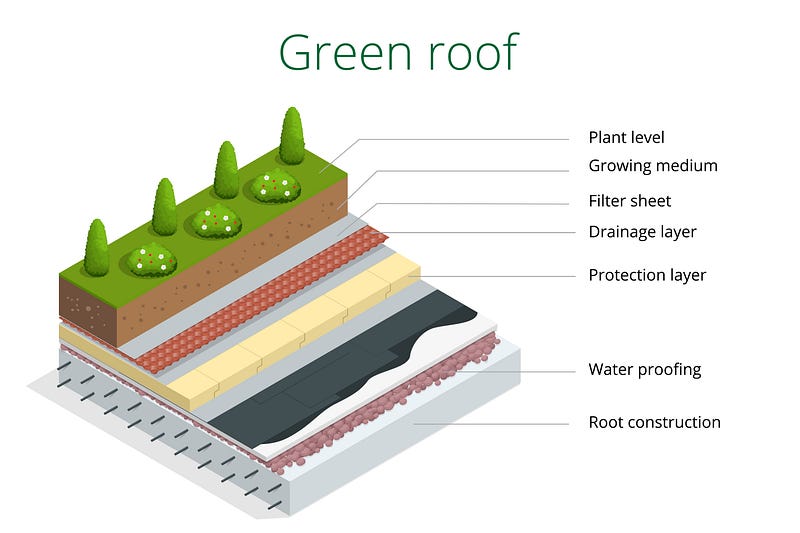
To counteract these effects, innovative solutions like green roofs have emerged. A green roof comprises layers of vegetation planted in soil, supported by a drainage system and protective layers for the building. The depth of the soil dictates the types of plants that can thrive.
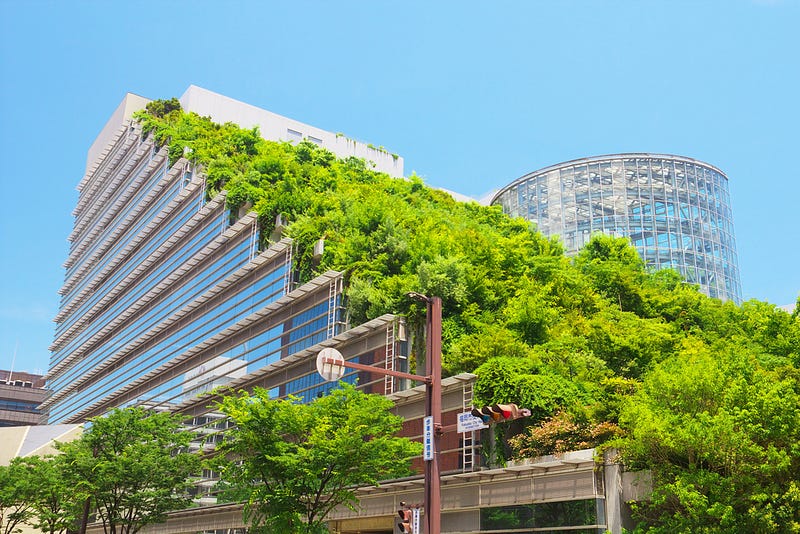

Chapter 2: Understanding Green Roofs and Their Benefits
Green roofs can be enhanced to create blue-green roofs, which include a water reservoir for improved water management. These roofs contribute significantly to the ecological balance and urban livability. Below are four key benefits they provide:
Section 2.1: Water Management
One of the primary advantages of green roofs, particularly blue-green roofs, is their ability to manage rainwater. The effectiveness of this system hinges on the soil depth and plant selection. Sedums are particularly effective as they retain substantial moisture and withstand drought conditions.
Green roofs absorb rainwater, reducing the risk of urban flooding. They can retain between 40% and 80% of annual rainfall, thus lessening the burden on drainage systems. Additionally, harvested rainwater can be reused for irrigation, sanitation, and even electricity generation, thereby enhancing the sustainability of urban water management.
Section 2.2: Energy Efficiency
Green roofs also play a vital role in regulating building temperatures, which lowers energy consumption. By cooling surfaces through evaporation and providing insulation, these roofs help mitigate urban heat. For instance, studies have shown that buildings with green roofs can be significantly cooler than those without.
Furthermore, blue-green roofs can harness stored water to generate renewable energy, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
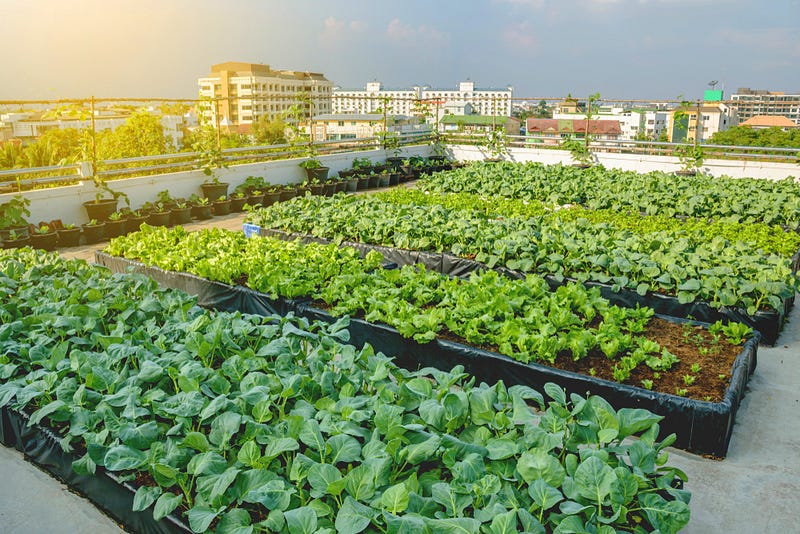
Section 2.3: Food Production
These roofs can also support urban agriculture, allowing cities to grow food in limited spaces. With urban land shrinking, utilizing rooftops for food production can alleviate pressure on local food systems. Crops such as lettuce, kale, and tomatoes thrive in the shallow soil of these roofs.
Growing food on rooftops not only provides fresh produce but also distances crops from industrial pollutants, contributing to healthier urban environments.

Section 2.4: Environmental Restoration
Green roofs also enhance urban environments by improving air quality and boosting biodiversity. They offer habitats for various plant and animal species, including essential pollinators like bees. The aesthetic and recreational benefits of these green spaces further enrich urban life.
Conclusion
In summary, both green and blue-green roofs foster urban resilience by managing water flow, cooling cities, and creating additional spaces for food production while enhancing air quality and biodiversity.
How to Promote Green Roofs
To advocate for more green roofs in your community, consider these actions:
- Engage with city planners about promoting green roof initiatives.
- Introduce garden spaces on existing roofs at home or work.
- Utilize rooftop areas for food cultivation.
- Implement water storage systems on green roofs to transition them into blue-green roofs.
Your thoughts and suggestions on promoting green roofs are welcome; please share them in the comments!
Credit
This article synthesizes insights from:
Cristiano, E., Deidda, R., & Viola, F. (2021). The role of green roofs in urban Water-Energy-Food-Ecosystem nexus: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 756, 143876.
Explore the importance of green roofs with Growing a Greener World Episode 122 - Green Roofs & Rooftop Gardens for an in-depth look at this innovative solution.
Learn more about the benefits of green roofs through Making It Grow - Moore Farms Botanical Garden's Green Roof.